THE HARMONY 2 | PHYTOESTROGENS
5.0 / 5.0
(1) 1 total reviews
Menopause & Menopause
Micronutrient complex
90 capsules
The Harmony is a collaboration with MAISON MADAME.
This exclusive micronutrient complex is especially for women during menopause and can alleviate the associated symptoms. Typical symptoms, in addition to hot flashes and sweats, are irregular menstrual bleeding, sleep disorders and mood swings. Many women become irritated more quickly, lack energy and suffer from weight gain.
With the power of, among other things, isoflavones (plant hormones), which are similar to female estrogen, your hormonal balance is supported in a natural way and counteracts the imbalance.
- This micronutrient complex of vitamins and isoflavones (plant hormones similar to female hormones) contributes to greater balance and harmony in your everyday life.
- Gender based
- Optimally combined for women
- Easy to swallow
- Can made from 100% recycled plastic and recyclable
- Regular price
-
€42,00 - Regular price
-
- Sale price
-
€42,00 - Unit price
-
€1.076,92 / per kg
Couldn't load pickup availability
Ready to ship immediately: Delivery time: 1-3 working days
Share


THE HARMONY 2 | PHYTOESTROGENS
- Regular price
-
€42,00 - Regular price
-
- Sale price
-
€42,00 - Unit price
-
€1.076,92 / per kg
DESCRIPTION & INGREDIENTS
Description
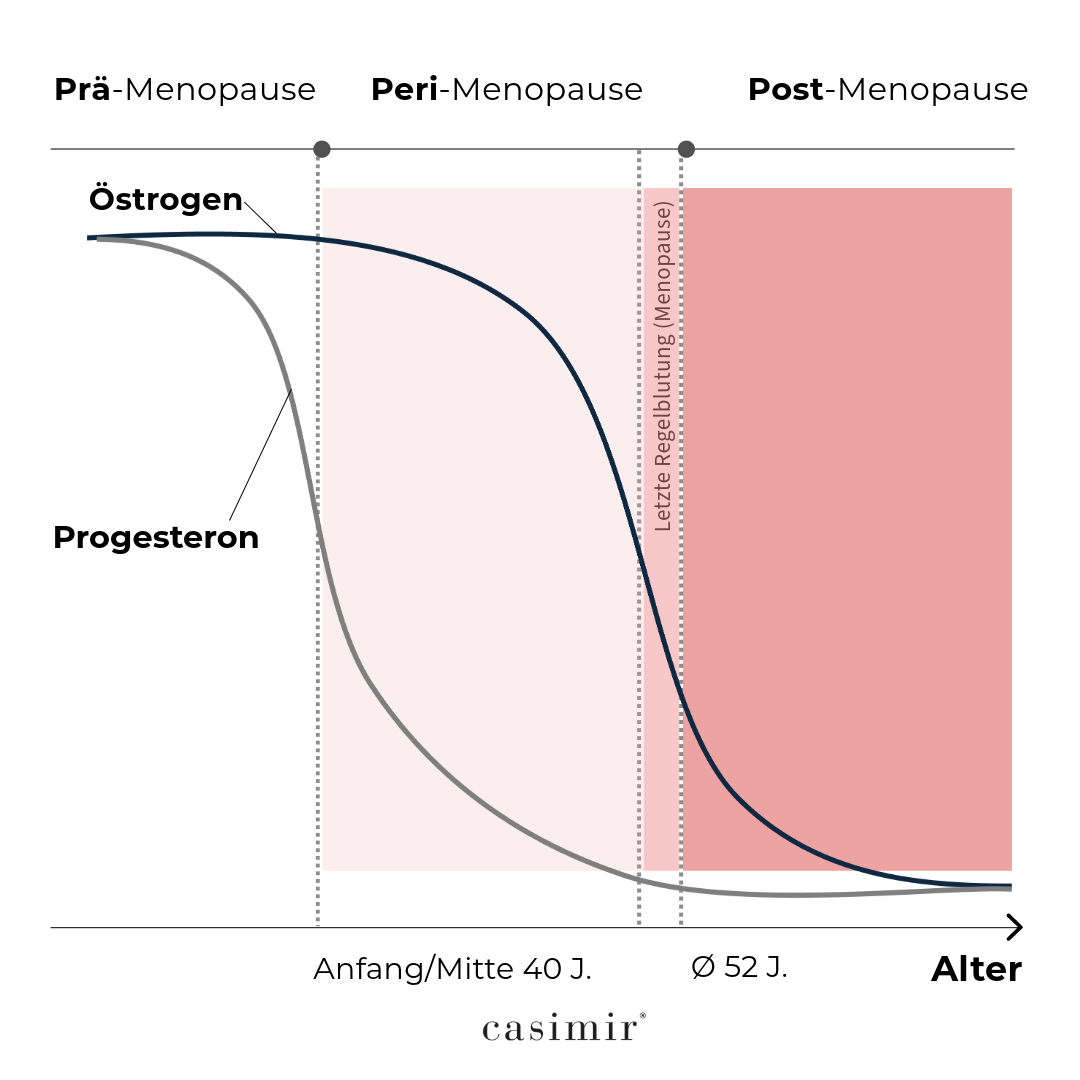
During menopause, hormone levels fluctuate. This can lead to various symptoms (see “About menopause and menopause”). With the help of plant hormones, the hormone level can be rebalanced.
Natural hormones are found particularly in red clover, yam, hops and pomegranate.
Since the terms can often be confused, we have listed and explained the most important terms here:
- Isoflavonesare from the group ofPhytoestrogens. These plant hormones are similar to the human hormone estrogen.
- Lignansare phytochemicals similar to the human hormone estrogen.
- Diosgeninis a plant-based active ingredient that is similar to human progesterone.
- Flavonesare the parent group ofFlavonoidsand these belong to the group ofPolyphenols. These are secondary plant substances with antioxidant effects that protect the human body from free radicals. They can also reduce the risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease. They have a positive effect on the immune system and can lower cholesterol levels.
About maca
Maca is also known as the “miracle tuber” from the Andes, where it is known as one of the oldest cultivated plants from Inca folk medicine. It belongs to the cruciferous family and is a good source of nutrients. It contains many proteins, omega-3 fatty acids, iron, iodine, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, zinc, calcium and vitamins. Due to its isoflavones (phytoestrogens), maca can be used to treat all symptoms related to female reproductive hormones. It supports hormonal imbalance and well-being. Maca is said to have a positive effect on inner restlessness, sleep disorders and hot flashes. The tuber is also said to stimulate sexual pleasure.
About flaxseed
Flaxseeds are the largest source of so-called plant lignans, which are similar to female estrogen and are intended to balance the estrogen balance. The lignans in flaxseed can work on both sides, breaking down too much estrogen and supporting too little. This can reduce hormone fluctuations and the resulting symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats and mood swings. Flaxseeds are also rich in fiber, which is highly recommended for a recommended high-fiber diet at this stage of life.
About red clover
Red clover is a clover plant and is part of the subgroup of butterflies, which belong to the legume family. It contains valuable nutrients such as magnesium, calcium, potassium, B1, B3 and vitamin C. Red clover is one of the isoflavones (plant hormones with estrogenic effects) and are also called phytoestrogens. They therefore have an effect on the regulation of the hormonal balance. When it comes to menopausal symptoms, red clover can have a positive effect on hot flashes, sweating, concentration, mood and sleep patterns.
A study from 2006 also showed that red clover extract has a positive effect on the mineral content of the bones and on the bone density of the thighs in women with estrogen deficiency.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ptr.2037
It must also be mentioned that red clover extract has a positive effect on the skin. It contains antioxidants that protect the skin from cell-damaging free radicals. Especially in connection with light-induced aging caused by UV rays. Red clover extract increases skin density and elasticity, which is also said to have an anti-aging effect and is also used for skin problems such as acne or eczema.
About yam
The yam is a tuber that is a staple food in Africa and South America, comparable to the potato. It has a high starch content, fiber and many other valuable micronutrients, such as vitamin C, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6 and B9, potassium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, manganese, iron and copper. It also has many antioxidants and can be described as a real superfood. An important ingredient, especially with regard to menopause, is the so-called diosgenin, a precursor to the human hormone progesterone, which counteracts estrogen dominance and regulates the unbalanced hormonal balance during menopause. Thousands of years ago, indigenous peoples used the yam to treat menstrual cramps or labor pains. The tuber also has an anti-inflammatory effect and is used for colds, inflammation, rheumatism and arthritis. Yam has an antispasmodic effect and has a positive effect on stress and inner restlessness. The high phosphorus content is important for bone strength, teeth and cells. Diosgenin also has a positive effect on memory performance.
About passionflower
The passion flower is a flowering plant and comes from North, South and Central America. Passionflower extract inhibits inner peace, overloaded nerves and promotes better sleep. The plant is known for its anti-anxiety properties. While it has long been used as a medicinal plant in its homeland, it was also discovered as a medicinal plant in Europe in the middle of the 20th century. The passion flower contains flavonoids (secondary plant substances) belonging to the polyphenols, which have an antioxidant effect. In addition, the plant has a direct effect on a neurotransmitter in the brain that prevents restlessness and tension.
About pomegranate
The pomegranate is also known as a symbol of fertility and has a positive effect on the body and mind, which has been proven in many studies. It contains iron, calcium, vitamins B, C and E. It is also rich in antioxidants, has an anti-inflammatory effect and can have a positive effect on cardiovascular diseases. The pomegranate peel as we use it also contains flavonoids (polyphenols) that help lower cholesterol levels. The fruit contains isoflavones or so-called phytoestrogens (plant hormones with estrogenic effects) and is used during menopause to provide hormone-regulating support. Symptoms such as hot flashes or mood swings can also be alleviated.
About hops
Hops are a genus of plants in the hemp family and can be found as a perennial in the northern hemisphere. Long before hops were used as an ingredient in beer, they actually became known as a medicinal plant. Hops have sleep-promoting and calming properties, which are very helpful for the symptoms of menopause. It is rich in the bitter substances humulone and lupulone and has flavonoids as well as a relatively large amount of isoflavones (plant hormones with estrogenic effects), also called phytoestrogens, which can affect the female hormonal balance. Flavonoids belong to the group of polyphenols (secondary plant substances) that have a positive effect on human health - they reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, have a positive effect on the immune system and are antioxidant. In addition, taking hop flower extract is said to relieve symptoms such as hot flashes. Hops are also considered antibacterial, appetite stimulating and digestive.
About vitamin B6
The entire fat metabolism, the immune system, the nervous system and the hormonal balance are controlled by vitamin B6, which also has positive effects on depression. Furthermore, it is
B6 is important for brain development, brain function and supports the production of serotonin, which has a positive impact on mood, sleep and well-being, especially on the subject of irritability.
Vitamin B6 contributes:
- to normal cysteine synthesis
- to normal energy metabolism
- to normal functioning of the nervous system
- to normal homocysteine metabolism
- to normal protein and glycogen metabolism
- to normal psychological function
- to normal production of red blood cells
- to normal function of the immune system
- to reduce tiredness and fatigue
- to regulate hormonal activity
Symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency:
- Skin inflammations
- fatigue
- Nerve irritation
Increased vitamin B6 requirement:
- pregnancy
- lactation
- high alcohol consumption
- certain medications
Vitamin B12
B12 is an all-rounder and takes over vital body functions. It is involved in many metabolic processes, such as energy production, the formation of red blood cells, maintaining the health of nerve cells, the production of DNA and RNA, and cell division. Like B6, B12 supports the production of serotonin, the so-called happiness hormone, which contributes to general well-being and a better mood. Both B vitamins are coordinated with each other and work best in combination.
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) contributes:
- to normal energy metabolism
- to normal functioning of the nervous system
- to normal homocysteine metabolism
- to normal psychological function
- to normal production of red blood cells
- to normal function of the immune system
- to reduce tiredness and fatigue
- to normal cell division
Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency:
- anemia
- fatigue
- Nervous disorders
Increased vitamin B12 requirements:
- Elderly people
- Vegetarians / Vegans
- in certain diseases
About Vitamin C
Vitamin C supports the immune system and protects cells. It also acts as an energy boost as it counteracts tiredness and exhaustion. Important in view of the listlessness and fatigue during menopause. Women during menopause have an increased need for vitamin C. Vitamin C is a kind of bouncer. It is involved in many processes in our body. The human body cannot produce vitamin C itself. Our vitamin C is from the natural extract of theacerola cherry,the third largest source of vitamin C in the world.
Vitamin C is one of the most important vitamins and contributes:
- to normal function of the immune system
- to reduce fatigue, as it is necessary for the production of adrenaline
- to protect cells from oxidative stress
- to normal energy metabolism
- to normal functioning of the nervous system
- to normal psychological function
- to improved iron absorption
- to normal collagen formation for normal function of blood vessels, bones, skin, gums, teeth and cartilage function
Increased vitamin C requirement:
- during pregnancy and while breastfeeding
- with regular and heavy physical exertion, especially in colder environments
- in smokers
- with vegetarian and vegan diets
- during sporting activity
About vitamin D3
D3, also commonly known as the sunshine vitamin, is the only vitamin that can be produced in the skin with the help of sunlight. Nevertheless, vitamin D3 deficiency is common in our latitudes, as around 60% of our skin surface should be exposed to sunlight for at least 15-30 minutes - ideally without sun protection. Vitamin D3 is important for strengthening a normally functioning immune system and is also recommended by the WHO* for the prevention of respiratory diseases. Dietary supplements cannot prevent COVID-19 diseases, but they can strengthen the immune system. According to a study, the mortality rate from COVID-19 diseases increases as vitamin D deficiency increases - the mortality risk of patients with vitamin D deficiency increases 10-fold.
With regard to menopause, vitamin D3 can significantly alleviate hot flashes, fatigue, depression and vaginal dryness. It also has a positive effect on mood and well-being. As women age, bone strength in particular decreases. D3 is known to strengthen bone density, which is particularly important for preventing osteoporosis.
Vitamin D3 is one of the most important vitamins and contributes:
- to normal function of the immune system (physical defense)
- to maintain normal muscle function
- to maintain normal bones
- to normal absorption/utilization of calcium
- to maintain normal teeth
- for the normal function of cell division
- to normal growth and development of children's bones
- to reduce the risk of falls. Falls are a risk factor for bone fractures
INCREASED VITAMIN D3 NEEDS:
- in children and older people
- in smokers
Vitamin K2
Unfortunately, due to falling estrogen levels, bone density is constantly decreasing. Vitamin K has a positive influence on bone health. Studies show that a vitamin K2 deficiency can lead to weaker bones and an increased risk of bone fractures. K2 prevents excess calcium deposits in the arteries and at the same time transports calcium into our bones, which is why it is particularly valuable.
Vitamin K2 is one of the most important vitamins and contributes:
- to normal blood clotting
- to maintain normal bones
ZUTATEN & HINWEISE
Zutaten:
Maca Wurzelextrakt, Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (Kapselhülle), Leinsamen Extrakt, Acerola Fruchtextrakt, Fenchel Samenextrakt, Granatapfel Schalenextrakt, Passionsblumen Blütenextrakt, Yamswurzel Extrakt, Hopfen Blütenextrakt, Menachinon, Pyridoxal-5'-phosphat, Cholecalciferol, Methylcobalamin.
Kapselhülle: Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose
Verzehrsempfehlung:
Je nach Bedarf ein bis zwei Kapseln pro Tag mit reichlich Wasser einnehmen.
Hinweise: Die angegebene empfohlene tägliche Verzehrsmenge darf nicht überschritten werden. Nahrungsergänzungsmittel sind kein Ersatz für eine ausgewogene, abwechslungsreiche Ernährung und eine gesunde Lebensweise. Außerhalb der Reichweite von kleinen Kindern aufbewahren. Kühl, trocken und lichtgeschützt lagern.
Die Einnahme von Phytoöstrogenen ist gemäß aktueller Leitlinie der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Gynäkologie und Geburtshilfe bei Frauen mit Zustand nach Brustkrebs nicht empfohlen.*
*https://register.awmf.org/assets/guidelines/015-062l_S3_HT_Peri-Postmenopause-Diagnostik-Interventionen_2021-01.pdf; https://www.krebsinformationsdienst.de/fachkreise/nachrichten/2019/fk08-soja-brustkrebs-ernaehrung-phytooestrogen.php
NUTRIENT VALUES
NUTRIENT REFERENCE VALUE (NRV):
|
ingredients |
per 1 capsule |
% NRV* |
% NRV ♀** |
per 2 capsules |
% NRV* |
% NRV ♀* |
| vitamin D3 | 0.75 μg | 15 | 4 | 1.5 μg | 30 | 8 |
| vitamin K2 | 11.25 μg | 15 | 19 | 22.5 μg | 30 | 38 |
| Acerola fruit extract | 60 mg | - | - | 120 mg | - | - |
| of which vitamin C | 24 mg | 30 | 25 | 48 mg | 60 | 50 |
| vitamin B6 | 1.4 mg | 100 | 100 | 2.8 mg | 200 | 200 |
| vitamin B12 | 0.375 μg | 15 | 9 | 0.75 μg | 30 | 18 |
| Maca root extract | 100 mg | - | - | 200 mg | - | - |
| flaxseed extract | 70 m g | - | - | 140 mg | - | - |
| of which lignans | 14 mg | - | - | 28 mg | - | - |
| fennel seed extract | 50 mg | - | - | 100 mg | - | - |
| pomegranate peel extract | 25 mg | - | - | 50 mg | - | - |
| of which ellagic acid | 10 mg | - | - | 20 mg | - | - |
| passionflower flower extract | 25 mg | - | - | 50 mg | - | - |
| of which flavonoids | 1 mg | - | - | 2 mg | - | - |
| yam root extract | 25 mg | - | - | 50 mg | - | - |
| of which diosgenin | 5 mg | - | - | 10 mg | - | - |
| hop flower extract | 20 mg | - | - | 40 mg | - | - |
| of which flavones | 0.8 mg | - | - | 1.6 mg | - | - |
*Reference quantity according to Regulation (EU) No. 1169/2011
**Reference amount for women according to DGE (= German Nutrition Society)
| Average nutritional values: | per 1 capsule | per 2 capsules | per 100 g |
| calorific value |
4 kJ |
7 kJ |
796 kJ |
| Fat hereof: saturated fatty acids |
< 0.5 g |
< 0.5 g 0 g |
1.8 g 0 g |
| carbohydrates of which sugar |
< 0.5 g |
< 0.5 g < 0.5 g |
33 g < 0.5 g |
| protein |
< 0.5 g |
< 0.5 g | 2.2 g |
| Salt |
0 g |
0 g | 0 g |
-
vegan
-
Nutrition Reference Value
-
Laboratory tested
-
without genetic technology
-
Gluten free
-
without palm oil
-
Lactose free
Nach drei Präparaten, die ich ausprobiert hatte, habe ich jetzt endlich eines gefunden, dass wirklich hilft. Nach vier Wochen waren die Hitzewallungen weg, ich kann wieder schlafen, die Stimmungsschwankungen sind besser und die Schleimhäute wieder befeuchtet. Ich bin darüber sehr froh, und werde es weiter nehmen.


