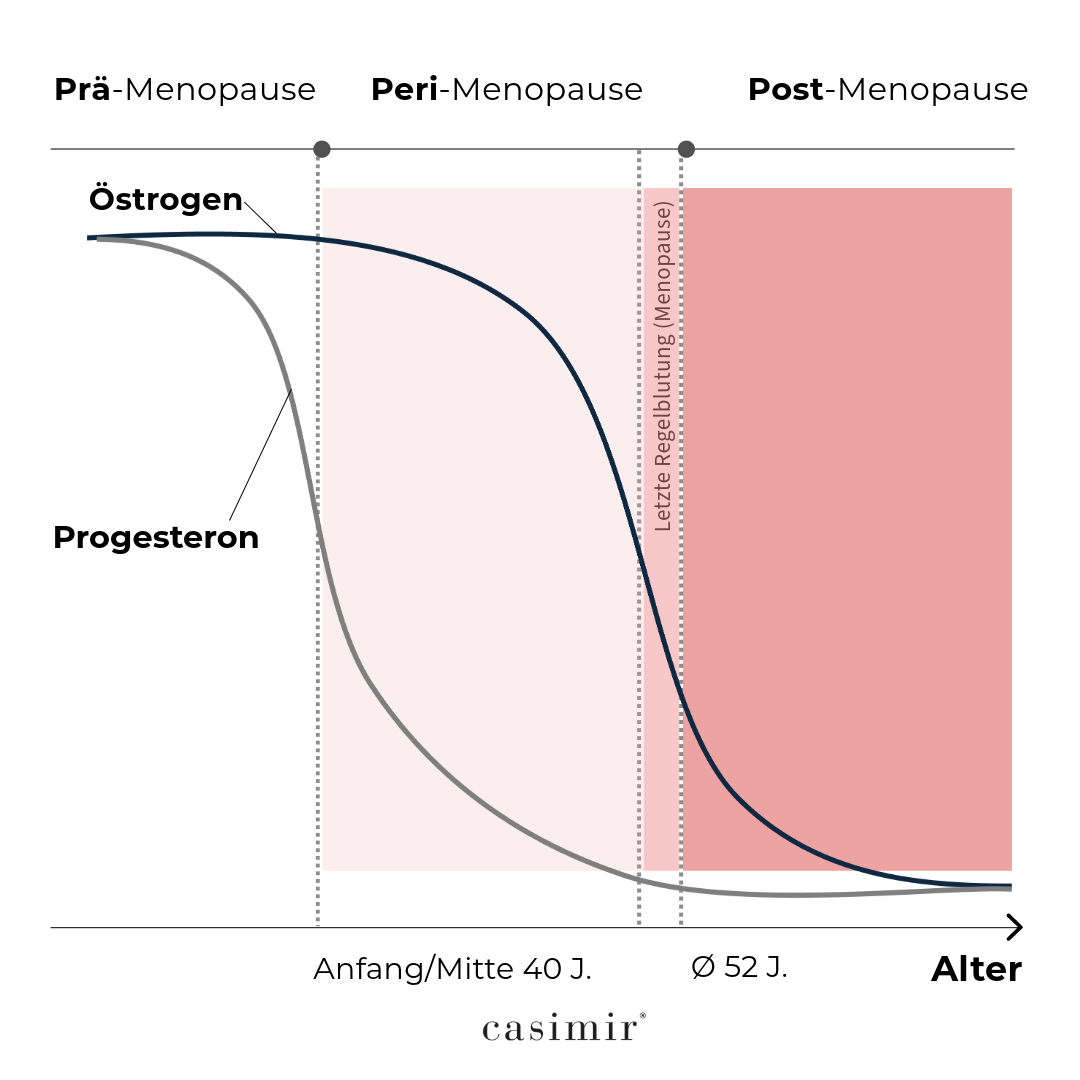
During menopause, hormone levels fluctuate. This can lead to various complaints (see “About menopause”). With the help of “plant hormones”, hormone levels can be rebalanced.
Secondary plant substances that are similar to human hormones are found particularly in red clover, yam, hops and pomegranate.
Since there can often be confusion about the terminology, we have listed and explained the most important terms here:
- isoflavonesandlignansare secondary plant substances from the group ofphytoestrogensThey are similar to the body’s own hormone estrogen in structure and effect, which is why the term “plant hormones” is derived from this.
- flavonesare the overarching group offlavonoidsand also belong to the group of phytoestrogens. These are secondary plant substances that are similar in structure and effect to the body's own hormone estrogen, but to a lesser extent. In addition to antioxidant properties that can protect the human body from free radicals, they are also said to have the properties of being able to reduce the risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease and cholesterol, and can have a positive effect on the immune system.
- diosgeninis a herbal active ingredient and a distant precursor of the human hormone progesterone. It is often used as a natural remedy to relieve symptoms of menopause. It also has antioxidant properties that can help protect cells from free radicals.
- progestinsare also hormones that belong to the female sex hormones. They are corpus luteum hormones that belong to the steroids. One of the most important representatives of the gestagens is progesterone. Progesterone belongs to the group of gestagens along with pregnanediol and pregnenolone.
About Yam
The yam root, also called yam or yams, is a tuber that is a staple food in Africa and South America, comparable to the potato. It has a high starch content, contains fiber and many other valuable micronutrients, such as vitamins C, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6 and B9, potassium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, manganese, iron and copper. It also contains many antioxidants and can be described as a real superfood. An important ingredient, especially with regard to the menopause, is the high proportion of diosgenin, a precursor of the human hormone progesterone, which counteracts estrogen dominance and regulates the unbalanced hormone levels during the menopause. Thousands of years ago, indigenous peoples used the yam root to treat menstrual cramps or labor pains. The tuber also has an anti-inflammatory effect and is used for colds, inflammation, rheumatism and arthritis. Yam has an antispasmodic effect and has a positive effect on stress and inner restlessness. The high phosphorus content is important for bone strength, teeth and cells. Diosgenin also has a positive effect on memory performance.
We use the yam root extract (the concentrated extract of the substance), which has a higher diosgenin content (20%).
About Fenugreek
Fenugreek, also known as Greek hay, is a plant from the Fabaceae family, the legume family, whose seeds and leaves are said to offer a variety of health benefits. It has been around for several thousand years and has been revered as a medicinal remedy ever since. Hildegard von Bingen and Sebastian Kneipp praised its supposed healing powers. It is used in medicinal medicine in China, India and Tibet. In herbal medicine it is used for diabetes mellitus, as it is said to lower blood sugar levels. Mothers with breastfeeding problems (although not recommended for breastfeeding mothers) use it in traditional medicine. It contains the amino acid histidine and the phytohormone diosgenin. Fenugreek is also a popular seasoning ingredient, used in a variety of forms in North African, Southern European and Asian cuisine. Fenugreek has a high protein content, contains fats, essential oils, bitter substances, valuable vitamins (especially vitamin A and all B vitamins, except B12) and important minerals (especially iron and magnesium). It is used for hair loss and skin problems and also contains many antioxidants. Its anti-inflammatory properties are also often used for inflammation. The healing substances of fenugreek are found in its seeds, which is why we use fenugreek seed extract (the concentrated extract of the seeds), which has a higher content of the ingredients.